Current location:Home > Product > Raw material of cosmeticss

|
Physical and Chemical Properties |
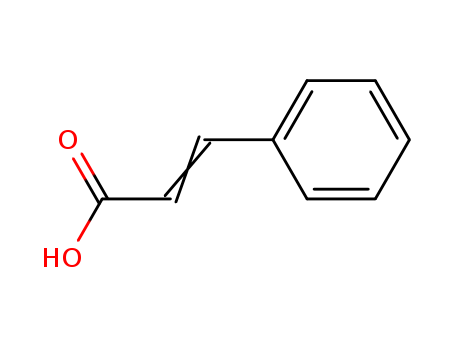
Cinnamic acid, also known benzal acetate, 3-phenyl-2-propenoic acid, belongs to a kind of unsaturated aromatic acid with a slight smell of cinnamon. It is presented in balsam, cinnamon oil and coca leaf in the form of free or ester form. Owing to the presence of a double bond, cinnamic acid has trans-/ cis-two isomers with the cis form containing an extra three kinds of homogeneous polycrystalline. Both trans-form and cis-form are in the presence of nature. The trans-form exists in the presence of essential oils including storax, cinnamon oil, Peruvian balsam, basil oil and cocoa leaves. The cis-form exists in Malacca galangal oil with the trans-form being more stable than the cis-form. The commercially available products are mostly in the form of trans. It has a relative molecular mass of 148.17. The first crystalline form of the cis form is called allocinnamic acid with the compound precipitated from water being monoclinic. It is colorless to white prismatic crystals with the relative density being 1.284 (4 ℃), the melting point being 42 ℃, the boiling point 265 ℃ (decomposition ) and 125 ℃ (2.533 × 103Pa); it is slightly soluble in water (25 ℃ when 0.937) but easily soluble in alcohol, ether and ethyl acetate. The second polymorph is called alpha-iso-cinnamic acid with the compound precipitated from ligroin being the monoclinic crystal. It is colorless to white prismatic crystals with the mp being 58 ℃ and the boiling point being 265 ℃. It is soluble in ethanol, acetic acid, chloroform and acetone and easily soluble in ether. The third polymorph is called beta-iso-cinnamic acid; it appears as monoclinic colorless to white prismatic crystals with the mp being 68 ℃. It is soluble in alcohol, ether, acetic acid, chloroform and acetone. Trans-isomer precipitated from dilute ethanol belongs to the monoclinic crystal and appears as white to pale yellow prismatic crystals with the relative density being 1.2475 (4 ℃), melting point being 133 ℃ and the boiling point being 300 ℃. It is very slightly soluble in water (25 ℃: 0.1; 98 ℃: 0.588), soluble in ethanol (25 ℃: 23), chloroform (15 ℃: 5.9), easily soluble in benzene, ether, acetone, acetic acid and carbon disulfide. When being distilled at 140 ℃, it undergoes decarboxylation to become styrene (Styrax BP). Upon oxidation, it generates benzoic acid. Both the cis-and trans-isomers have flower honey aroma with sweet and spicy flavor. Rat-Oral LD50: 2500 mg/kg. |
|
Role and purpose |
Cinnamic acid is an important kind of organic synthetic raw material. It is mainly used for the synthesis of methyl cinnamate, ethyl cinnamate and cinnamic acid benzyl ester. It is widely used in the perfume industry and the pharmaceutical industry. In medicine, it has been ever used as an insect repellent. Cinnamic acid was used as spices for the preparation of cherry, apricot, honey and cinnamon aromas and flavors; it can also be used as the starting material of cinnamic acid ester. The GB2760-1996 of our country provided that cinnamic acid is allowable edible spices; in addition, it can also be used as the raw material of photosensitive resin poly vinyl cinnamic acid series; it can also be used as the raw material for the synthesis of methyl, ethyl and benzyl esters. These esters, being used as fragrances, can be applied to cosmetics and soap, it can also be used as a local anesthetic, hemostatic agents and pharmaceuticals (lactic acid Prenylamine and baclofen, etc.) raw materials; cinnamic acid may also be used as plant growth regulators and raw materials of pesticides; anti-corrosion agents of fruit and vegetables; raw material of ultraviolet agent and photosensitive resin for cosmetic sunscreen. Cinnamic acid may also be used as the standard for organic trace analysis and determination of double bond, determination of uranium and vanadium and thorium separation. |
|
Preparation |
Cinnamic acid is also produced by Knoevenagel condensation of benzaldehyde with malonic acid in the presence of weakly basic catalysts, such as ammonia and amines. Reflux together 10ml of benzaldehyde with 10gm of malonic acid and 40ml of 8% ethanolic ammonia solution placed in a 100ml round bottom flask fitted with a reflux condensor on water bath till a clear solution is obtained (about 8-10hours). Set the assembly for downward distillation and distill off the excess alcohol. Continue heating the residual oily portion until the evolution of carbon dioxide ceases. Dissolve the residue in 20ml water, cool and add dilute hydrochloric acid till acidic. Collect the precipitated unsaturated acid on buchner funnel,wash with cold water. Recrystallise from hot water and collect crystals of cinnamic acid, m.p 132°C. Synthesis of cinnamic acid from benzaldehyde |
|
Content Analysis |
Accurately weigh 500 mg of sample which have been previously dried for 3 hours in drier filled with silica gel; add 0.1mol/L hydrogen. |
|
Toxicity |
GRAS (FEMA). The acute oral LD50 in rats is 2.5 g/kg, and the acute dermal LD50 in rabbits exceeds 5 g/kg. Cinnamic acid applied neat to intact or abraded rabbit skin for 24 h was slightly irritating;a4% solution in petrolatum produced no sensitization in man. |
|
Limited use |
FEMA (mg/kg): Soft drinks 31; Cold drink 40; Confectionery 30; Bakery 36; Gum 10. Take moderate as the limit (FDA§172.515, 2000). |
|
Production method |
Commercial synthesis of cinnamic acid almost always results in the trans isomer. The Perkin reaction is the oldest known method of producing cinnamic acid commercially. In this reaction benzaldehyde [100-52-7] is condensed with acetic anhydride in the presence of sodium acetate as catalyst. Benzal chloride reacts with alkali acetate in an alkaline medium to give a high yield of cinnamic acid. Cinnamic acid can be obtained by this reaction in the presence of amines such as pyridine in more than 80 % yield. It can also be prepared through: mixing the benzoylacetone, sodium carbonate and bleach, generating sodium cinnamic acid, followed by processing with sulfate. |
|
Synthesis Reference(s) |
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 75, p. 1068, 1953 DOI: 10.1021/ja01101a016The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 59, p. 710, 1994 DOI: 10.1021/jo00083a006 |
|
Safety Profile |
Poison by intravenous and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by ingestion. A skin irritant. Combustible liquid. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and fumes. |
|
Synthesis |
Rainer Ludwig Claisen (1851–1930), German chemist, described for the first time in 1890 the synthesis of cinnamates by reacting aromatic aldehydes with esters. The reaction is known as the Claisen condensation. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: A monocarboxylic acid that consists of acrylic acid bearing a phenyl substituent at the 3-position. It is found in Cinnamomum cassia. |
InChI:InChI=1/C9H8O2/c10-9(11)7-6-8-4-2-1-3-5-8/h1-7H,(H,10,11)/b7-6-
The chemical functionality within porous...
Heterobimetallic complexes containing ti...
Available online Two new acid salts were...
The reactions between [CuCl2(PPh3)2] and...
Here we report a facile approach to prep...
(Figure Presented) The coordinatively un...
An effective metal organic framework (MO...
Aerobic selective oxidation of allylic a...
-
Cascade reactions represent an atom-econ...
The Perkin condensation of benzaldehyde ...
Cyclomaltohexaose (α-cyclodextrin) and c...
Recently, irreversible inhibitors have a...
The number of deaths or critical health ...
Chlorination with chlorine is straightfo...
The invention discloses a synthesis meth...
cinnamaldehyde-(O-[1]naphthylcarbamoyl oxime )
furan-2,3,5(4H)-trione pyridine (1:1)

1,3-dinaphthalen-1-ylurea

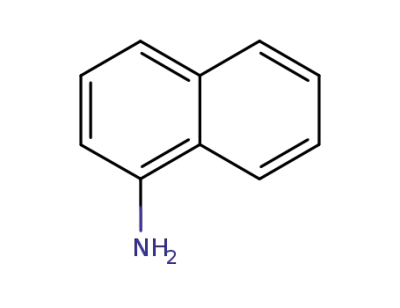
1-amino-naphthalene

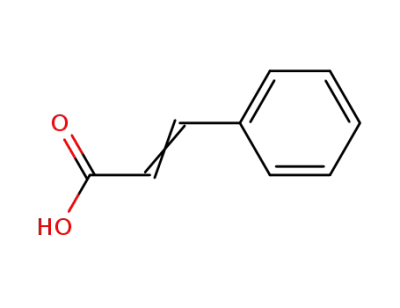
Cinnamic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
α-naphthylcarbamic acid-derivative of β-cinnamaldoxime;
|
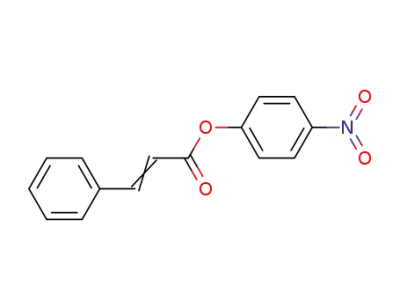
4-nitro-phenyl cinnamate

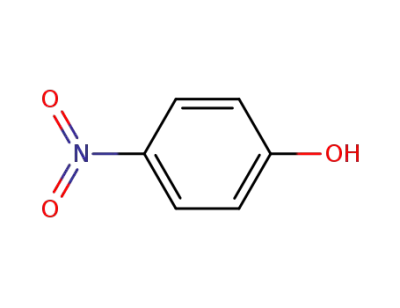
4-nitro-phenol


Cinnamic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
hydroxide;
In
1,4-dioxane; water;
at 50 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
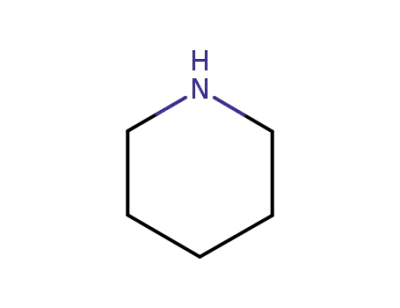
piperidine
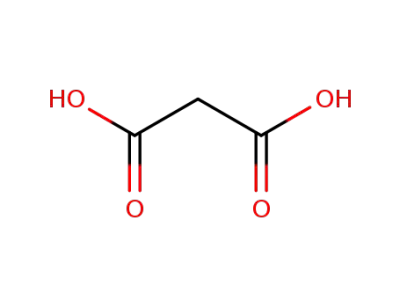
malonic acid
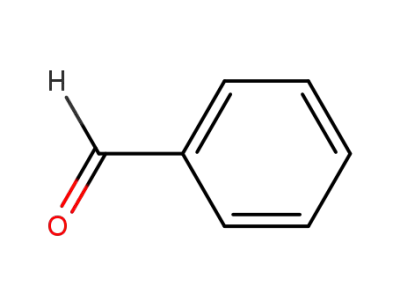
benzaldehyde
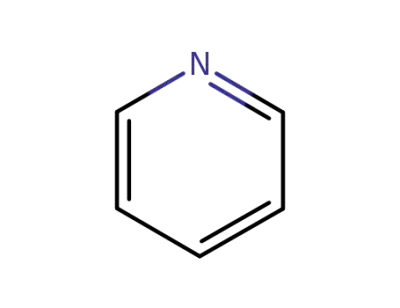
pyridine
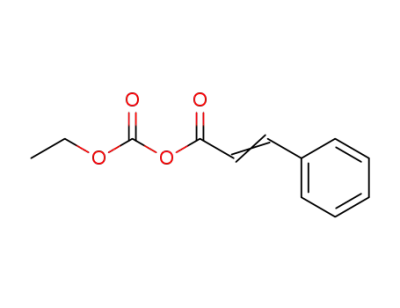
(carbonic acid ethyl ester)-cinnamic acid-anhydride
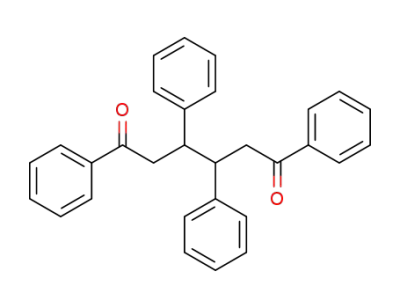
1,3,4,6-tetraphenylhexane-1,6-dione
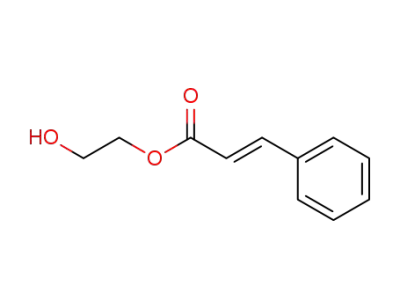
2-hydroxyethyl 3-(phenyl)-2-propenoate
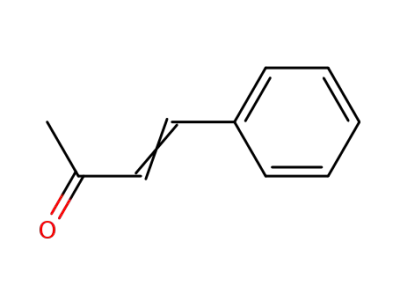
1-Phenylbut-1-en-3-one