Current location:Home > Product > Pesticides and waste materials

|
Physical properties |
Pure product is a colorless, hexagonal crystal or white powder. Commercial grade material may be grayish-black powder or lump (the color is due to presence of calcium carbide and other impurities); density 2.29 g/cm3; melts around 1,340°C; sublimes around 1,150 to 1,200°C on rapid heating; reacts with water. |
|
Definition |
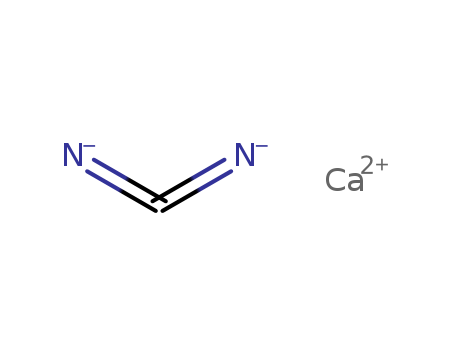
ChEBI: The calcium salt of cyanamide, formed when calcium carbide reacts with nitrogen |
|
Production Methods |
Calcium cyanamide was first produced commercially around 1900 as a fertilizer. The process of making calcium cyanamide involves three raw materials—coke, coal, and limestone— plus nitrogen. The limestone (calcium carbonate) is burned with coal to produce calcium oxide. The calcium oxide is then allowed to react with amorphous carbon in the furnace at 2000°C with the formation of calcium carbide (CaC2). Finely powdered calcium carbide is heated to 1000°C in an electric furnace into which pure nitrogen is passed. It is then removed and uncombined calcium carbide removed by leaching. |
|
Preparation |
Calcium cyanamide is prepared from calcium carbide. The carbide powder is heated at about 1,000°C in an electric furnace into which nitrogen is passed for several hours. The product is cooled to ambient temperatures and any unreacted carbide is leached out cautiously with water. CaC2 + N2 → CaCN2 + C (ΔH?°= –69.0 kcal/mol at 25°C) |
|
General Description |
A colorless to gray, odorless solid. May cause illness from ingestion. May irritate the skin. If exposed to water or high temperatures, calcium cyanamide may generate toxic and flammable fumes. Used to make pesticides and in fertilizers. |
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Depending on the calcium carbide content, the cyanamide reacts with water (moisture from air or soil) to produce acetylene and hydrated calcium oxide or calcium hydroxide. Absorption of water during handling or storage of technical calcium cyanamide may cause explosion [Pieri, M. Chem. Abs. 46, 8335 1952]. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
When hydrated CALCIUM CARBIDE generates salts of calcium that are basic and are generally soluble in water. The resulting solutions contain moderate concentrations of hydroxide ions and have pH's greater than 7.0. They react as bases to neutralize acids. These neutralizations generate heat, but less or far less than is generated by neutralization of the bases in reactivity group 10 (Bases) and the neutralization of amines. They usually do not react as either oxidizing agents or reducing agents but such behavior is not impossible. |
|
Hazard |
Fire risk with moisture or combined with calcium carbide. Skin, eye, and upper respiratory tract irritant. Questionable carcinogen. |
|
Health Hazard |
Inhalation or contact with vapors, substance or decomposition products may cause severe injury or death. May produce corrosive solutions on contact with water. Fire will produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control may cause pollution. |
|
Fire Hazard |
Produce flammable gases on contact with water. May ignite on contact with water or moist air. Some react vigorously or explosively on contact with water. May be ignited by heat, sparks or flames. May re-ignite after fire is extinguished. Some are transported in highly flammable liquids. Runoff may create fire or explosion hazard. |
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Nonflammable |
|
Agricultural Uses |
Calcium cyanamide (CaCN2) is a dark colored, granulated material containing around 21 % nitrogen. Its dark color is due to the presence of calcium carbide. Calcium cyanamide is produced by heating a mixture of limestone with coal in a nitrogen atmosphere. Generally, the process is carried out in three steps. In the first step, calcium carbonate (limestone) is decomposed at about 1100°C. In the second step, calcium oxide (CaO) and coke (or coal) are heated in an electric furnace to produce calcium carbide. The final step involves heating the powdered calcium carbide at about 1100°C with pure nitrogen (produced by liquefaction of air and fractional distillation) to produce calcium cyanamide. The fertilizer-grade calcium cyanamide contains 21 % nitrogen, 11 % calcium, 11 % free carbon, 5% oil, 2 to 4% water and oxides of aluminum, iron and silicon. In the presence of moisture and air, calcium dicyandiamide (a poisonous compound) is formed. It distinctly leaves alkalinity in the soil equivalent to 1.3 kg calcium carbonate (CaCO3) per 0.45 kg of nitrogen applied. At pH 7 or below, calcium dicyandiamide is converted into urea and lime within one week of its being in the soil. When dry, calcium cyanamide is dusty but it is generally used as granules. It is poisonous, irritating to the skin and used as a pesticide, fertilizer and defoliant in cotton. It is as good a fertilizer as sodium nitrate or ammonium sulphate, but not as fast acting. Calcium cyanamide is an excellent weed killer, especially for tobacco plants, when applied 2 to 3 weeks before sowing. It is also used for producing melamine, urea and certain cyanide salts. |
|
Safety Profile |
Poison by ingestion, inhalation, sh contact, intravenous, and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic to humans by ingestion. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data. Mutation data reported. The fatal dose, by ingestion, is probably around 20 to 30 g for an adult. It does not have a cyanide effect. Calcium cyanamide is not believed to have a cumulative action. Flammable. Reaction with water forms the explosive acetylene gas. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx and CN-. See also CALCIUM COMPOUNDS, AMIDES, and CYANIDE |
|
Potential Exposure |
Calcium cyanamide is used in agriculture as a fertilizer, herbicide; defoliant for cotton plants; and pesticide. It is also used in the manufacture of dicyandiamide and calcium cyanide as a desulfurizer in the iron and steel industry; and in steel hardening. |
|
Carcinogenicity |
Calcium cyanamide was weakly mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium strain TA1535 and nonmutagenic in strain TA100. |
|
Shipping |
UN1403 Calcium cyanamide with .1% calcium carbide, Hazard Class: 4.3; Labels: 4.3-Dangerous when wet material |
|
Incompatibilities |
Commercial grades of calcium cyanamide may contain calcium carbide; contact with any form of moisture solutions may cause decomposition, liberating explosive acetylene gas and ammonia. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. May polymerize in water or alkaline solutions to dicyanamide. Contact with all solvents tested also causes decomposition |
InChI:InChI=1/CH2N2.Ca/c2-1-3;/h2H2;/q;+2
Various metals, such as Ca, Mg, Al, Ti, ...
Single crystals of Ca11N6[CN2]2 (dark re...
Solid state metathesis reactions can be ...
Solid state reactions of tungsten(IV) ch...

hydrogen cyanide

calcium oxide

carbon monoxide

hydrogen

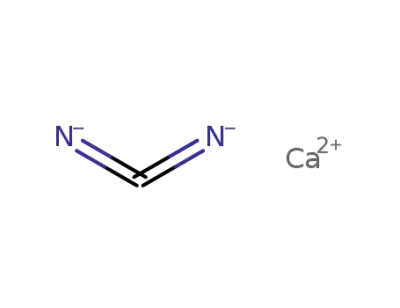
calcium cyanamide
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
In
neat (no solvent);
equilibrium; at 800°C on right side;; pure product;;
|
99% |
|
In
neat (no solvent);
equilibrium; at 800°C on right side;; pure product;;
|
99% |
|
In
neat (no solvent);
|
|
|
In
neat (no solvent);
|
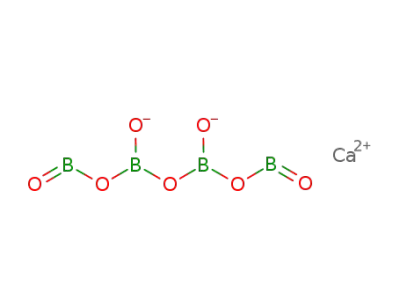
calcium pyroborate


pyrographite

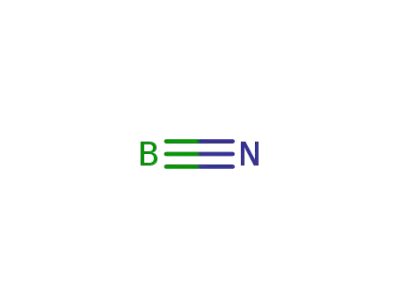
boron nitride


calcium cyanamide
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
nitrogen;
byproducts: CO; at 1800°C and cooling to 1400°C, or at 1850°C for 30 min. and 1400°C for 15 min.;
|
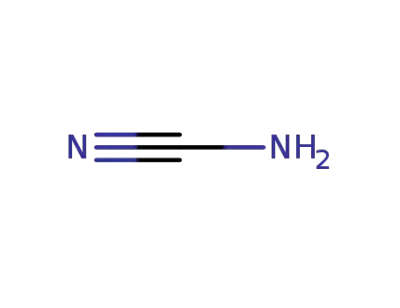
CYANAMID
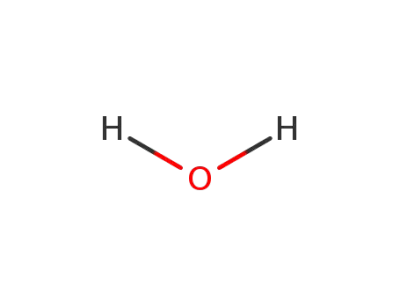
water

hydrogen cyanide
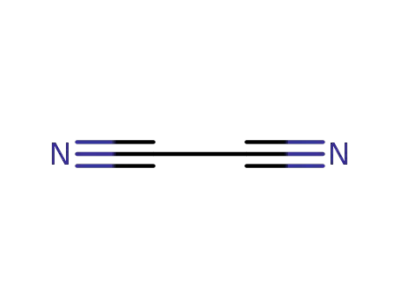
ethanedinitrile

CYANAMID
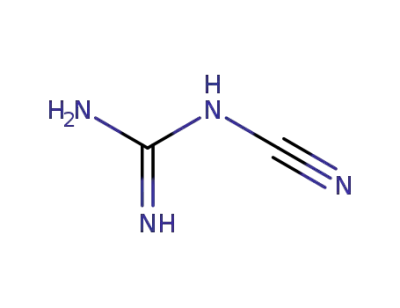
N-Cyanoguanidine
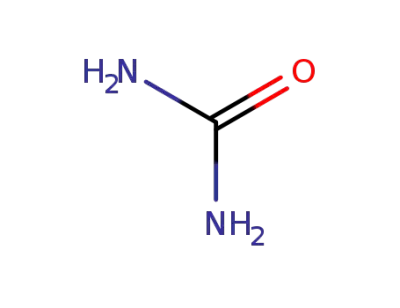
urea
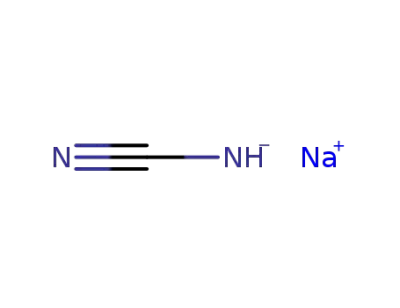
sodium cyanamide