Current location:Home > Product > Auxiliary antioxidant

|
Chemical Description |
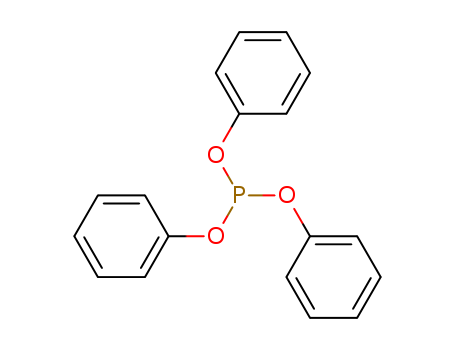
Triphenyl phosphite is an organophosphorus compound that is used as a reagent in organic synthesis. |
|
Secondary antioxidants |
Triphenyl phosphite is called for short TPP, it is also known as triphenoxytitanium phosphine, it is phosphite-based compound, it is a secondary antioxidant, it has light stabilizing effect, it is applicable to polyvinyl chloride, polypropylene, polystyrene, poly acetate, ABS resin, epoxy resin and the like. Triphenyl phosphite is widely used as polyvinyl chloride chelating agent, when the metal soap is used as stabilizer, coordinating with this product can reduce the harm of the metal chlorides, it can keep transparency of product and inhibit the change in color. Further triphenyl phosphate is also used as flame retardant plasticizer. Phosphite phenyl diisooctyl can be obtained by the transesterification reaction of triphenyl phosphite and isooctanol in the presence of catalyst, phosphite phenyl diisooctyl can be used as secondary antioxidant. It has good resistance to discoloration, it can increase oxidation resistance and light stability. It has chelating action in PVC, low toxicity, it can be used in plastic medical devices. In addition, this product in the presence of sodium methoxide can proceed the transesterification reaction with methanol to form trimethyl phosphite. Triphenyl phosphite is as raw material, it can react with octanol in the solution of sodium methoxide, octyl diphenyl phosphite can be prepared. The above information are collated by Xiaonan edit lookchem (2016-12-03). |
|
Physical and chemical properties |
It is colorless or pale yellow oily liquid. It has slightly with phenol odor. Molecular weight is 310. Color (APHA) <50. Acid value is <0.5mgKOH/g. Phosphorus content is 10%. The relative density is 1. 180~1.186 (25°/ 15.5℃). Viscosity is 12 mPa?s (38℃), 4.5mPa?s (99℃). The freezing point is 19~24℃. Melting point is 22~25℃. Boiling point is 220℃ (1333Pa). Flash point (open cup) is 218.3℃, ignition point is 243℃. Refractive index is 1.5880 ~1.5900 (25℃). Solubility (g/100g solvent): methanol> 10, benzene> 10 acetone> 10, it is insoluble in water. Triphenyl phosphate has irritating to the skin, rat oral LD50 is 2800mg/kg body weight, it is used as polymer antioxidant and stabilizer, it has better synergy effect with many phenolic antioxidants. By effect of phosphorus trichloride and phenol can get triphenyl phosphite. |
|
Chemical properties |
It is colorless to pale yellow monoclinic crystal below room temperature. It is colorless light yellow transparent oily liquid at room temperature or higher, it has pungent odor. It is insoluble in water, soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, ethyl ether, acetone, benzene and the like. |
|
Production methods |
It can be obtained from phenol and phosphorus trichloride. Raw material consumption (kg/t) phenol (freezing point ≥40.4 ℃) 940 phosphorus trichloride (99%) 480 |
|
Toxic Effects |
The primary toxic effects of triphenyl phosphite are exerted on the nervous system of susceptible animals. The univeral signs of triphenyl phosphite neurotoxicity result from the irreversible inhibition of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) at cholinergic synapses in the central, peripheral and autonomic nervous system. Triphenyl phosphite is also capable of producing characteristic delayed neurotoxic effects that are manifested several days or weeks after even minimal drug exposure. Such actions are not related to AChE inhibition and the precise biochemical mechanism(s) leading to the delayed neurotoxicity symptoms are largely unresolved. |
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Insoluble in water. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
Organophosphates, such as Triphenyl phosphite, are susceptible to formation of highly toxic and flammable phosphine gas in the presence of strong reducing agents such as hydrides. Partial oxidation by oxidizing agents may result in the release of toxic phosphorus oxides. |
|
Health Hazard |
Triphenyl phosphite (TPP) is a skin irritant and sensitizer in humans and is neurotoxic in laboratory animals.Systemic effects have not been reported in humans. |
|
Safety Profile |
Poison by intraperitoneal and subcutaneous routes. Moderately toxic by ingestion. An experimental eye and severe human skin irritant. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame. To fight fire, use CO2, mist, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of POx. See also PHENOL. |
|
Purification Methods |
Its ethereal solution is washed succesively with aqueous 5% NaOH, distilled water and saturated aqueous NaCl, then dried with Na2SO4 and distilled under vacuum after evaporating the diethyl ether. [Walsh J Am Chem Soc 81 3023 1959, Verkade & Coskren in Organo Phosphorus Compounds (Kosolapoff & Maier eds) Wiley Vol 6 pp 211-577 1973, Beilstein 6 IV 695.] |
InChI:InChI=1/C18H15O3P/c1-4-10-16(11-5-1)19-22(20-17-12-6-2-7-13-17)21-18-14-8-3-9-15-18/h1-15H
Spallation neutron and high-energy X-ray...
The rates of dissociation of the unique ...
Efficient synthesis of o-borylphenols is...
-
-
Triaryl phosphites selectively reduce ar...
Elaboration of the η2-acyl ligand in hyd...
-
A series of ammonium monosubstituted H-p...
-
-
Six tris(aryloxy)phosphorothionates subs...
The products of electrolysis in dipolar ...
Treatment of phosphine-boranes with mole...
Industrially important triaryl phosphite...
A method for preparing phosphate ester d...
Acylpeptide hydrolase is a serine protea...
Flow synthesis techniques have received ...
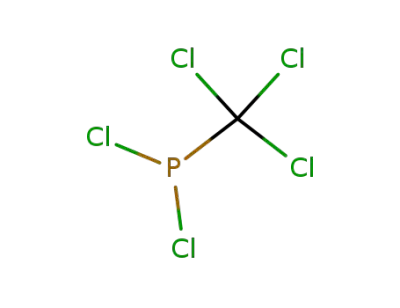
trichloromethylphosphonous dichloride
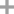
phenol

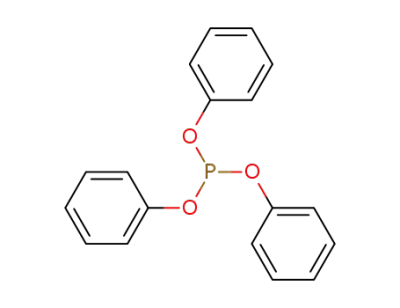
triphenyl phosphite

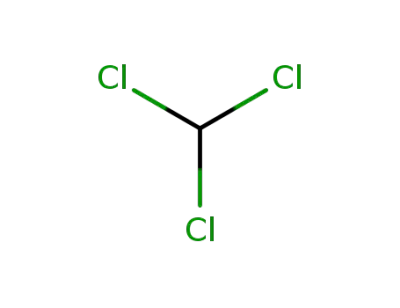
chloroform

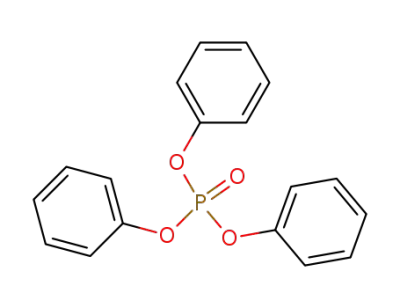
phosphoric acid triphenyl ester
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
|
6.7% 34% 55.6% |
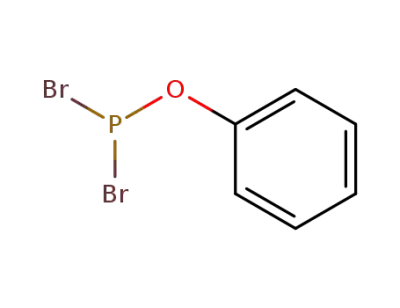
phenyl dibromophosphite


triphenyl phosphite

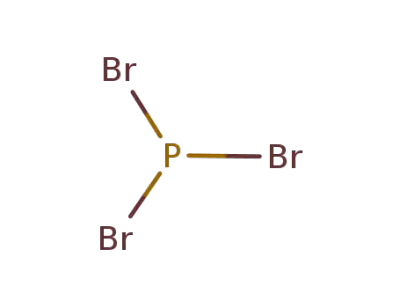
phosphorus tribromide
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
beim Erwaermen;
|

phenol
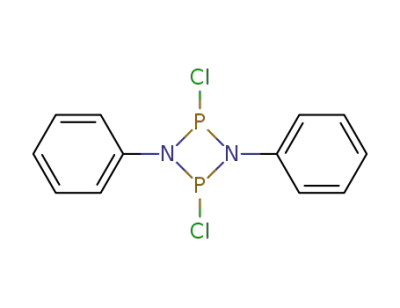
2,4-dichloro-1,3-diphenyl-cyclodiphosphazane
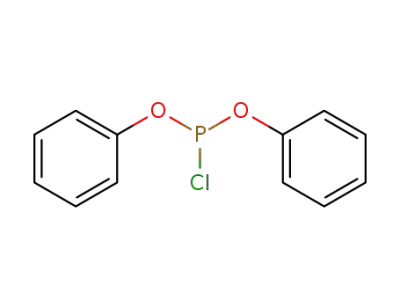
Diphenyl phosphorochloridite
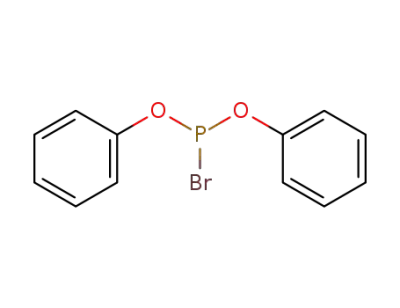
diphenyl bromophosphite
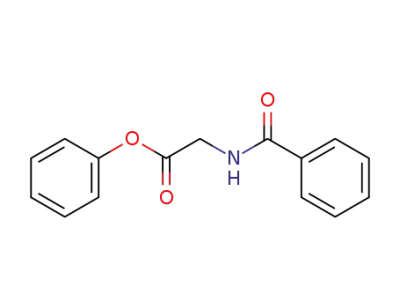
phenyl hippurate
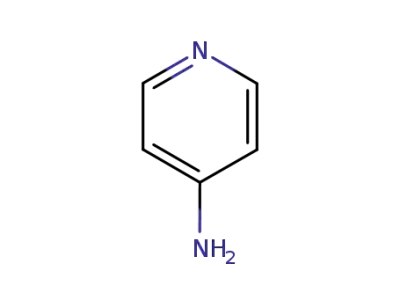
4-aminopyridine
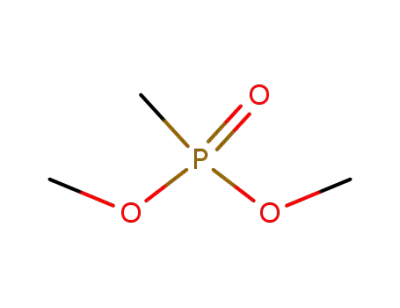
dimethyl methane phosphonate
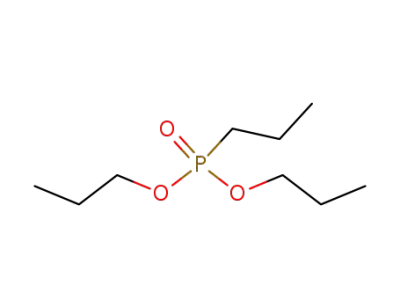
dipropyl propylphosphonate