Current location:Home > Product > Vitamins and amino acids

|
Chemical Description |
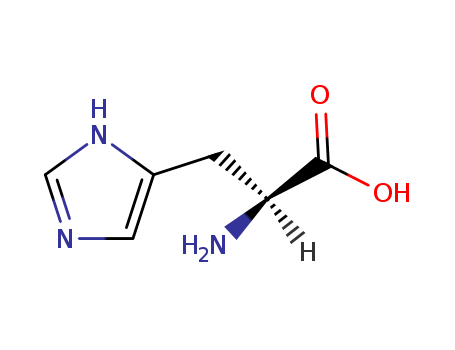
Histidine is an alpha-amino acid containing an isopyrazole ring. It is a constituent amino acid of body proteins and is found in some functional proteins such as histones and hemoglobin. |
|
Physiological Functions |
Histidine is a natural chelating agent and is involved in the structure and function of many enzymes. |
|
Molecular Interactions |
The versatility of histidine in molecular interactions arises from its unique molecular structure. Histidine's imidazole side chain can engage in various molecular interactions, including cation-π interaction, π-π stacking interaction, hydrogen-π interaction, coordinate bond interaction, and hydrogen bond interaction. These interactions contribute to histidine's role in protein structure, enzymatic function, and other physiological processes. |
|
Nutritional and Therapeutic Uses |
Histidine is considered an essential amino acid for young children but non-essential for adults. It has been used as a nutritional supplement in various conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, anaemia in chronic renal failure, fatigue during exercise, ageing-related disorders, metabolic syndrome, atopic dermatitis, ulcers, inflammatory bowel diseases, ocular diseases, and neurological disorders. |
|
General Description |
Histidine is an essential amino acid that is crucial for the synthesis of proteins in the human body. It plays a key role in the growth and repair of tissues, as well as in the maintenance of the myelin sheath that protects nerve cells. Additionally, histidine is a precursor for the synthesis of histamine, which is involved in various physiological processes such as digestion, immune response, and inflammation. It also acts as a metal chelator, binding with heavy metals to aid in their excretion from the body. Histidine is found in various protein-rich foods such as meat, fish, dairy products, and certain grains, making it an important nutrient for overall health and well-being. |
InChI:InChI:1S/C6H9N3O2/c7-5(6(10)11)1-4-2-8-3-9-4/h2-3,5H,1,7H2,(H,8,9)(H,10,11)
An unusual trans cleavage reaction was o...
Asymmetric transformation reaction of L-...
Amino acids are key synthetic building b...
Strategic replacement of protons with fl...
Described are methods and compositions f...
l-Carnosine (l-Car, β-alanyl-l-histidine...
Hizikia fusiformis lectine

L-alanin

L-Cysteine

L-threonine

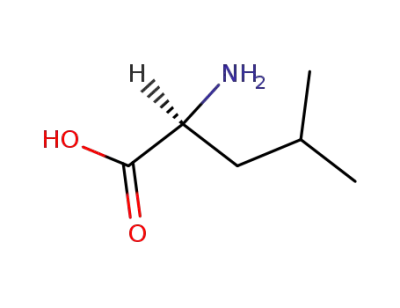
L-leucine

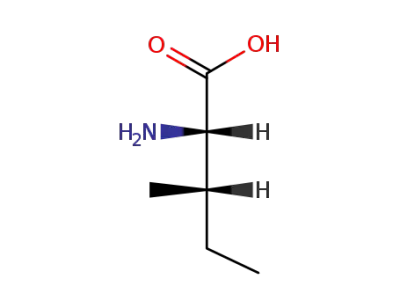
L-isoleucine

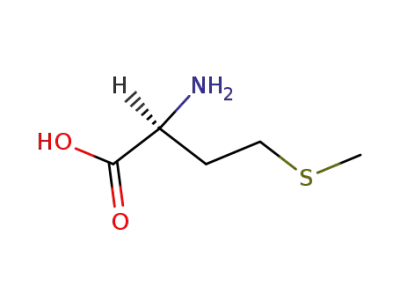
L-methionine

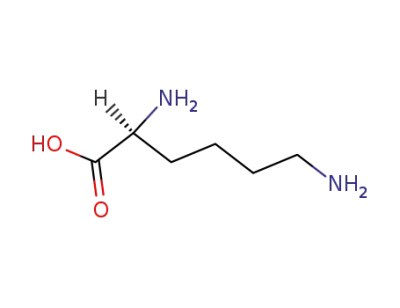
L-lysine

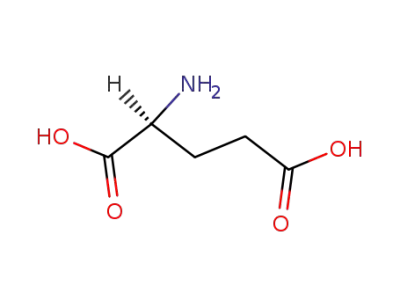
L-glutamic acid

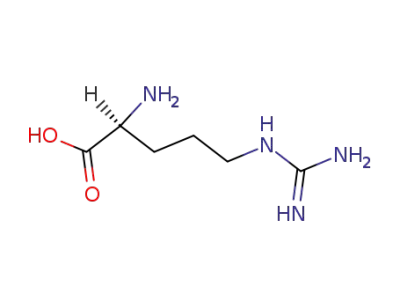
L-arginine

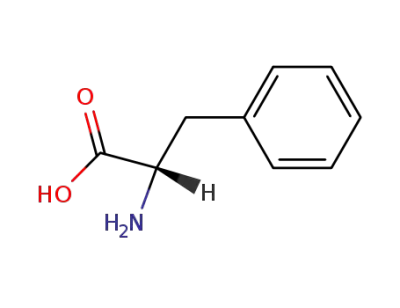
L-phenylalanine

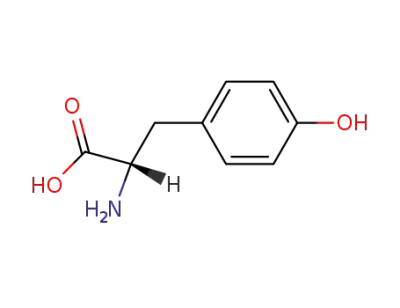
L-tyrosine

L-proline

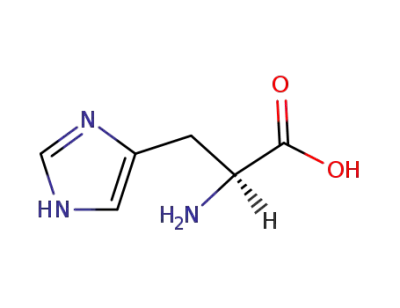
L-histidine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
hydrogenchloride;
In
water;
at 100 ℃;
for 24h;
Inert atmosphere;
Sealed tube;
|
type I collagen from Bester sturgeon scales


L-alanin

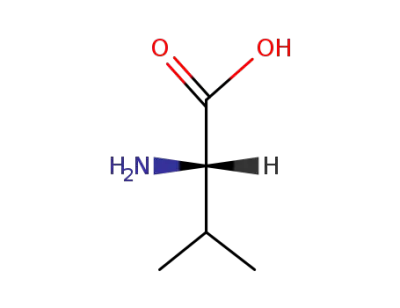
L-valine

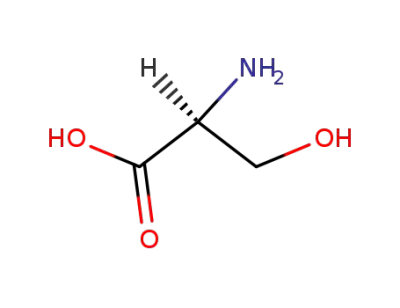
L-serin


L-threonine


L-leucine


L-isoleucine


L-methionine


L-lysine

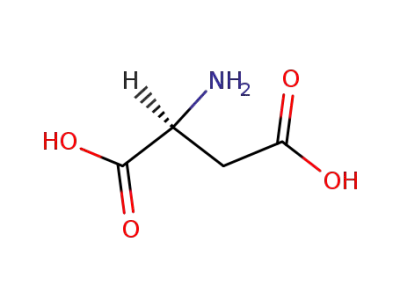
L-Aspartic acid

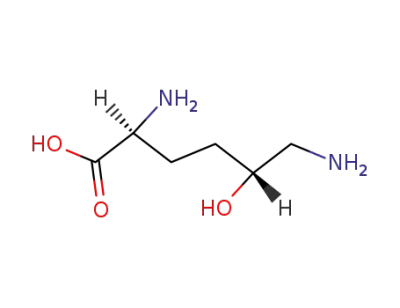
(5R)-5-hydroxy-L-lysine


L-arginine

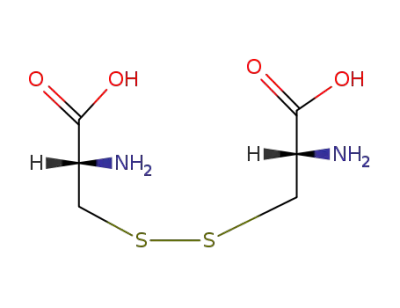
S,S-cystine


L-phenylalanine


L-tyrosine

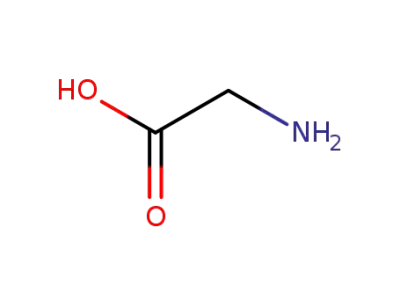
glycine

L-proline

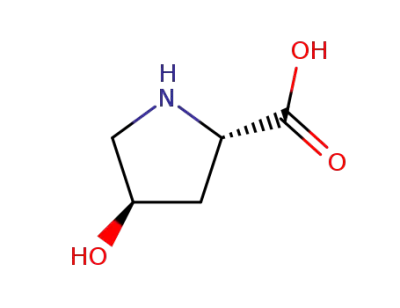
4R-4-hydroxyproline


L-histidine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
hydrogenchloride; water;
at 110 ℃;
for 24h;
|
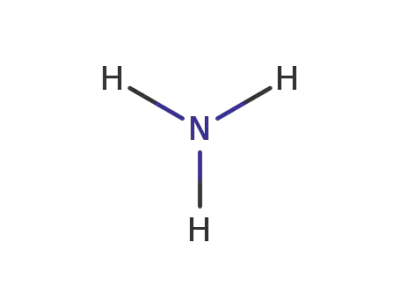
ammonia
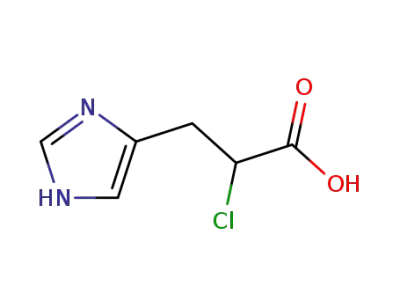
2-chloro-3-(1H-imidazol-4-yl)propanoic acid
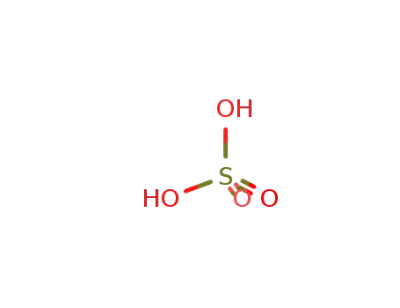
sulfuric acid
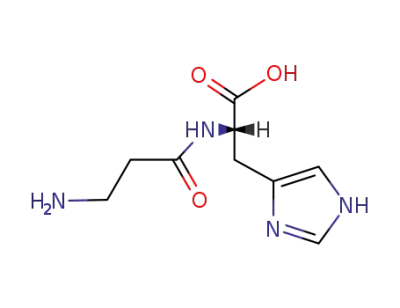
Carnosine
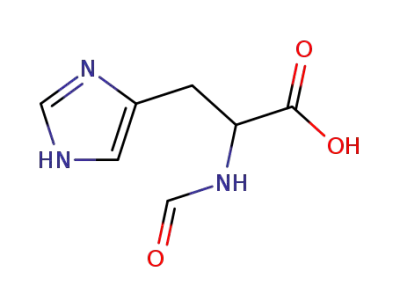
Nα-formyl-histidine
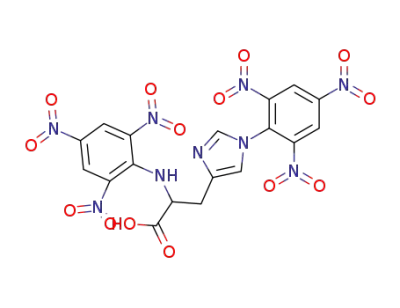
1,Nα-dipicryl-histidine
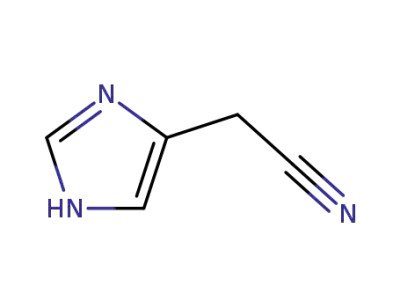
4-cyanomethylimidazole
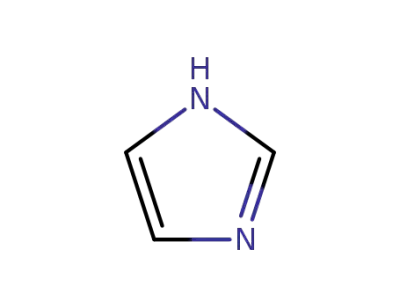
1H-imidazole